The most suitable heat sink substrate for LED - aluminum nitride ceramic substrate
Date:2018-07-12
At present, with the development of LED industry at home and abroad in the direction of high efficiency, high density, high power, etc., it can be seen from 2017 to 2018 that the overall domestic LED has made rapid progress, and the power is also getting bigger and bigger, development performance. Superior heat dissipation materials have become a top priority for solving LED heat dissipation problems.
At present, with the development of LED industry at home and abroad in the direction of high efficiency, high density, high power, etc., it can be seen from 2017 to 2018 that the overall domestic LED has made rapid progress, the power is also getting bigger and bigger, and the development performance is superior. Heat dissipation materials have become a top priority for solving LED heat dissipation problems. In general, LED luminous efficiency and service life will decrease with the increase of junction temperature. When the junction temperature reaches above 125 °C, the LED may even fail. In order to keep the LED junction temperature at a lower temperature, it is necessary to use a high thermal conductivity, low thermal resistance heat sink substrate material and a reasonable packaging process to reduce the overall package thermal resistance of the LED.
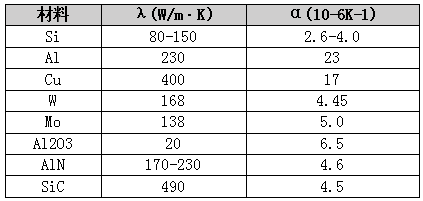
At present, the commonly used substrate materials are Si, metal and metal alloy materials, ceramics and composite materials. Their thermal expansion coefficients and thermal conductivity are shown in the following table. Among them, the cost of Si material is high; the intrinsic conductivity of metal and metal alloy materials, the coefficient of thermal expansion are not matched with the chip material; the defects of ceramic materials are difficult to process, and it is difficult to meet various performance requirements of high-power substrates at the same time.
Since the development of power LED packaging technology, the available heat dissipation substrates mainly include epoxy resin copper-clad substrates, metal-based copper-clad substrates, metal-based composite substrates, and ceramic copper-clad substrates.
Epoxy copper-clad substrates are the most widely used substrates in traditional electronic packaging. It plays the role of support, conduction and insulation. Its main characteristics are: low cost, high moisture absorption resistance, low density, easy processing, easy realization of micro-pattern circuits, suitable for large-scale production. However, since the base material of FR-4 is epoxy resin, the thermal conductivity of organic materials is low and the high temperature resistance is poor. Therefore, FR-4 cannot meet the requirements of high-density, high-power LED packaging, and is generally only used in low-power LED packages.
The metal-based copper-clad substrate is a novel substrate that appears after FR-4. The copper foil circuit and the polymer insulating layer are directly bonded by a thermally conductive bonding material and a metal and a base having a high thermal conductivity, and the thermal conductivity is about 1.12 W/m·K, compared with FR-. 4 has a big improvement. Due to its excellent heat dissipation, it has become the most widely used product in the market of high-power LED heat-dissipating substrates. However, it also has its inherent disadvantages: the thermal conductivity of the polymer insulation layer is low, only 0.3 W/m·K, which causes the heat to pass directly from the chip to the metal base; the thermal expansion coefficient of the metal Cu and Al Larger, may cause more serious thermal mismatch problems.
The most representative material for the metal matrix composite substrate is aluminum silicon carbide. Aluminum SiC is a metal matrix composite that combines the low expansion coefficient of SiC ceramics with the high thermal conductivity of metal Al. It combines the advantages of two materials, with low density, low thermal expansion coefficient, high thermal conductivity, and high stiffness. A series of excellent features. The thermal expansion coefficient of AlSiC can be adjusted by changing the SiC content to match the thermal expansion coefficient of adjacent materials to minimize the thermal stress of both.
Ceramic substrate materials are mainly Al2O3, aluminum nitride, SiC, BN, BeO, Si3N4, etc. Compared with other substrate materials, ceramic substrates have the following characteristics in mechanical properties, electrical properties, and thermal properties:
(1) Mechanical properties. Mechanical strength, can be used as a support member; good processability, high dimensional accuracy; smooth surface, no microcracks, bending, etc.
(2) Thermal properties. The thermal conductivity is large, the thermal expansion coefficient is matched with chip materials such as Si and GaAs, and the heat resistance is good.
(3) Electrical properties. The dielectric constant is low, the dielectric loss is small, the insulation resistance and the insulation are high, and the performance is stable under high temperature and high humidity conditions, and the reliability is high.
(4) Other properties. Good chemical stability, no hygroscopicity; oil and chemical resistance; non-toxic, pollution-free, α-ray emission is small; crystal structure is stable, it is not easy to change in the temperature range; raw material resources are abundant.
For a long time, Al2O3 and BeO ceramics are two main substrate materials for high power packaging. However, the two substrate materials have inherent disadvantages. The thermal conductivity of Al2O3 is low, and the thermal expansion coefficient is not matched with the chip material. Although BeO has excellent comprehensive performance, it has high production cost and is highly toxic.
Therefore, from the aspects of performance, cost and environmental protection, neither of these substrate materials can be used as the most ideal material for the development of high-power LED devices in the future. Aluminum nitride ceramics have excellent properties such as high thermal conductivity, high strength, high electrical resistivity, low density, low dielectric constant, non-toxicity, and thermal expansion coefficient matched with Si, and will gradually replace traditional high-power LED substrate materials. The most promising ceramic substrate material in the future.
【Close】




 +86-760-22115926 Anna Zhang
+86-760-22115926 Anna Zhang
 gaea668@263.net
gaea668@263.net